I. WHAT ARE CLEFT SENTENCES?

Generally speaking, a cleft sentence is a sentence that is split (cleft) so as to put the focus on one part of it only. This means that cleft sentences are complex sentences (two simple sentences together) used to emphasize one particular part.
USING “IT”
We can use the pronoun “ it”, at the beginning of a cleft sentence, to emphasize one element of the whole sentence. For instance:
- It was your father who used your computer.
- It’s the fridge that doesn’t work.
- It was at night that my parents arrived.
USING “IT’S NO USE or THERE’S NO USE”
- It’s no use arguing with your neighbors. It was not really their fault.
- There’s no use (in) arguing with your neighbors. It was not really their fault.
USING OTHER CONNECTORS
Some other connectors that characterize cleft sentences are: the reason why, the thing that, the person/people who, the place where, the day when. Here are some examples:
1) The reason why I have to call your father is to let him know of your health problem - OR
It´s to let your father know of your health problem that I have to call him.
2) The thing that made Stephany angry was not being told the truth. OR
- It was not being told the truth that made Stephany angry.
- What made Stephany angry was not being told the truth.
- All that made Stephany angry was not being told the truth.
3) The person who took the wallet was Sandra. – OR
- It was Sandra who took the wallet.
4) The place where Stephany left the new books was at her Mother´s. OR
- It was at her Mother´s that Stephany left the new books.
5) The day (that) I have to go to the dentist is Monday, not Tuesday. OR
- It´s Monday when I have to go to the dentist.
- It´s on Monday that I have to go to the dentist.
USING “ WHAT CLAUSES”
We use this structure when we want to focus on the verb or verb phrase. We can use an infinitive with or without the preposition “to”. For example:
- What Stephany did was (to) talk to her children.
- All Stephany did was (to) talk to her children.
- What you should do is SPEND more time with your family.
- What he did was (to) let his employees organize the festival all on their own.
- All he did was (to) let his employees organize the festival all on their own.
USING “WHAT HAPPENS- WHAT HAPPENED”
Lastly, these structures are used when the emphasis is on the whole sentence and not only on just one part of it. For instance:
- What happened was that Mr. Downey didn´t want to attend the party.
- What happens is that Joe Downy doesn´t like parties.
II. CONSOLIDATION.
III. EXERCISE I.
IV. READING TEXT.
READING COMPREHENSION AND VOCABULARY BUILDING
Read the text below and decide which answer (A,B,C or D) best fits each gap. Use higher case letters (mayúsculas).

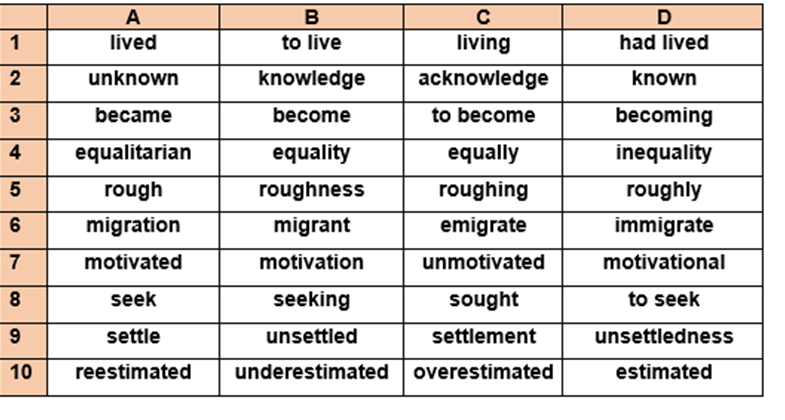
V. BIBLIOGRAPHY
Azar, B. S., Azar, D.A., & Koch R.S. (2009). Understanding and Using English Grammar. Longman.
Barker C. and Mitchell, L. (2004). Mega 1 (First Ed.). Macmillan Publishers.
Hewings, M. (2013) Advanced Grammar in Use with Answers: A Self-Study Reference and Practice Book for Advanced Learners of English. Cambridge University Press.
Murphy, R. (2012). English Grammar in Use. Ernst Klett Sprachen.
Murray, L. (2014) English Grammar. Cambridge University Press.
VI. WEB RESOURCES
Images_Compra propia de licencias de banco de imágenes de Pixton y Pngtree, exentas de derechos de autor. https://www-es.pixton.com/ & https://es.pngtree.com/free-backgrounds.
ReadingText_ Evason, Nina (2018) Mexicans in Australia. The Cultural Atlas. Retrieved from https://culturalatlas.sbs.com.au/mexican-culture/mexican-culture-mexicans-in-australia#mexican-culture-mexicans-in-australia. Educational institutions and/or government may be permitted to copy publications, audio and/or audio-visual files from the Cultural Atlas in accordance with the Copyright Act 1968.
VII. CREDITS
- All practice exercises and charts were written by Connie Reyes_2022_ENES- LEÓN-UNAM
- Audio version performed by Kimberly, Isabella, John and Matt_Compra propia de licencia de uso de voces en Voicemaker, exenta de derechos de autor. https://voicemaker.in/ _Connie Reyes Cruz_2022_