I. WHAT DO ADVERBS DO IN A SENTENCE IN ENGLISH?

They add information to something else in a sentence. For instance:
a) They describe verbs or actions. For example:
- Richard rides his motorcycle carefully.
- (The adverb “carefully” describes how the boy rides his motorcycle. It is adding information to the verb).
b) Adverbs are also phrases that describe adjectives. For instance:
- It was a really exciting trip.
(“Really” adds info to the adjective “exciting”)
- It is too hot in here.
(“Too” adds info to the adjective “hot”)
c) They describe other adverbs. Example:
- Mom works incredibly hard.
(The adverb “incredibly” is describing the adverb “hard”)
d) They also serve to show when, where or how often something happens.(last week, last year,this morning, for the last 6 months, in a strange way, etc.)
- Let`s meet the girls at noon.
- My brother moved to London last year.
e) Adverbs help us to describe situations, like in:
- Ignazio's obviously the best of the singers we`ve heard so far.
- Fortunately, we were able to catch the plane.
In summary, ADVERBS….
- describe verbs
- describe adjectives
- describe other adverbs
- describe whole sentences
II. HOW MANY KINDS OF ADVERBS ARE THERE?
In general, there are 5 categories of adverbs.

1) Adverbs of time and place describe WHERE or WHEN something happens (here, there, nearby, yesterday, in an hour). These come AT THE END of the sentence or phrase.
- Hang in there. They´ll meet you in half an hour.
- Is there a mall nearby?
If both (time and place adverbs) appear in a sentence, adverbs of place go BEFORE adverbs of time.
- My boss was here about ten minutes ago.
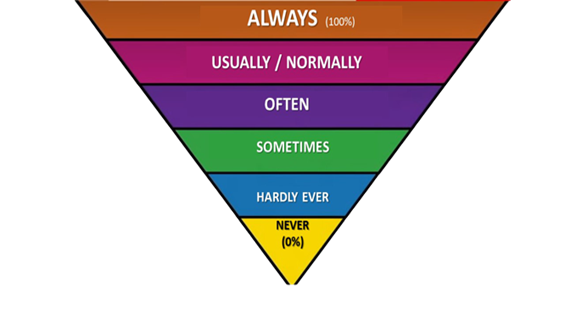
2) Adverbs of frequency describe HOW OFTEN something happens (often, sometimes, always, never, hardly ever). They usually come BEFORE the main verb. However, if the main verb is BE, adverbs of frequency go after it.
- Mom almost always gets up early. She hardly ever gets up late.
- Dad isn´t usually talkative, but Mom is usually sociable.
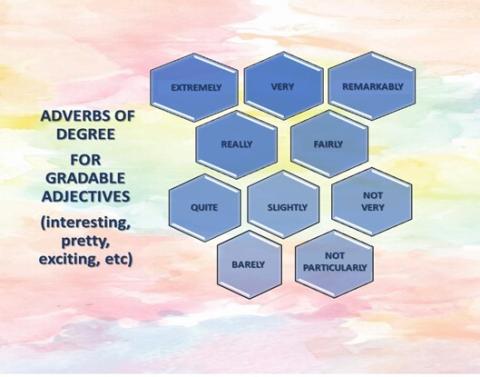
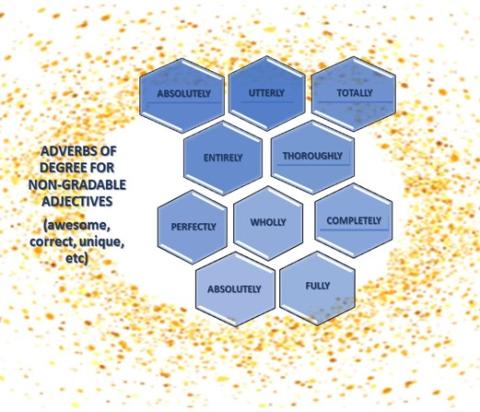
3) Adverbs of degree mostly describe other adjectives or adverbs and answer the question TO WHAT EXTENT something happens (very, too, little, absolutely, really). They come BEFORE the word they describe.
- It`s absolutely a zoo in there!
- My parents took the news really calmy.
4) Adverbs of manner describe a verb or how someone does something (fast, well, skillfully). They come AFTER the verb or verb phrase which they describe.
- My brother drives slowly and carefully.
- My sister didn´t do well on her job interview.
5) Remark-adverbs describe a whole sentence or situation. They usually come AT THE BEGINNING of a sentence.
- Basically, your project has been completed.
- Eventually, they had to admit they were in love with each other.
- Unfortunately, his father couldn´t attend the wedding.
III. SOME QUICK RULES TO REMEMBER

1) Many adverbs end in “LY” _ Beautifully, quickly, slowly, clearly, naturally, etc.
2) If the adjective ends in -Y change it to -ILY to make it an adverb.
- angry--->angrily
- happy--->happily
- healthy--->healthily
3) There are other irregular adverbs which have different forms as adjectives and change completely when used as adverbs. So what`s the adverb for good?
- Good ---> Well
- He`s a good writer. ( “Good” is an adjective)
- He writes well. (“Well” is an adverb describing how he writes)
- Some adverbs are irregular (fast, better). These adverbs do not change their form. They are the same when used as adjectives or adverbs, depending on the word they describe.
- Adelle`s a really fast worker.
(adjective”fast” modifying the noun “worker”).
- Jessica works really fast.
(adverb “fast” describing the action _ or verb_ how she works).
- Ignazio´s a better singer than the others.
(adjective “better” modifying “singer”).
- Paolo sings better than the others.
(adverb “better” describing how she sings).

IN CONCLUSION:
Adjectives---> describe nouns
Adverbs---> describe everything else: verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and whole
sentences.
IV. CONSOLIDATION. NOW TRY THE FOLLOWING QUIZ.
Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentences correctly.
V. LANGUAGE USE PRACTICE
ADVERBS
Review the adverbs of frequency.
EXERCISE II. Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentences correctly.
VI. READING COMPREHENSION AND VOCABULARY BUILDING
PRACTICE I. Read the text below and choose the correct word for each space. For each statement, mark the correct answer.
|
1 |
eclipsed |
hidden |
masked |
hermetic |
|
2 |
touristically |
tours |
tourism |
touristy |
|
3 |
graphic |
decorative |
picturesque |
skillful |
|
4 |
everywhere |
nowhere |
somewhere |
universally |
|
5 |
traditional |
acceptable |
widespread |
ancestral |
|
6 |
neighboring |
next-door |
proximate |
beside |
|
7 |
beyond |
further |
away from |
long way off |
|
8 |
round |
past |
through |
in the middle |
|
9 |
produces |
conceives |
causes |
makes |
|
10 |
scene |
section |
spot |
locality |
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Azar, B. S., Azar, D.A., & Koch R.S. (2009). Understanding and Using English Grammar. Longman.
Barker C. and Mitchell, L. (2004). Mega 1 (First Ed.). Macmillan Publishers.
Hewings, M. (2013) Advanced Grammar in Use with Answers: A Self-Study Reference and Practice Book for Advanced Learners of English. Cambridge University Press.
Murphy, R. (2012). English Grammar in Use. Ernst Klett Sprachen.
Murray, L. (2014) English Grammar. Cambridge University Press.
Berry, R. (2018). English grammar. Routledge.
Leech, G., & Svartvik, J. (2013). A communicative grammar of English. Routledge.
WEB RESOURCES
Image 1_Free stock photos_ https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-man-riding-bicycle-4054069/ Photo by Nick Wehrli.
Image 2_Free stock photos_https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-person-holding-alarm-clock-1028741/ Photo by Acharaporn Kamornboonyarush from Pexels
Image 3_Free stock photos_pixabay.com.es.idea-3082824_960_720_ Robin Higgins
Image 4_ Free stock photos_pixabay.com.es. idea 2-2681503_960_720
CREDITS
- (2021) Practice exercise written by Connie Reyes-Cruz_Language Department at ENES-LEON UNAM
- Audio version performed by Sally and Matthew_Voicemaker_Text to Speech Converter_Connie Reyes 2022 Subscription
- Story by Miriam -info.talesofvisuals@gmail.com_Proudly created with Wix.com. Text retrieved and adapted from _https://www.wix.com/blog/2021/02/types-of-blogs/#viewer-akoj2 in https://www.talesofisrael.com/.
- Practice exercise written by Connie Reyes-Cruz_ Language Department at ENES-LEON UNAM
- Free stock photos_https://www.pexels.com/photo/people-walking-on-seashore-2102650/ Photo by Haley Black from Pexels